Enterprise architecture focuses on achieving business outcomes and value realization through effective solution definition and deployment. It encompasses various aspects, including services management and operations, but is not limited to technology management.
In alignment with the ITIL framework, ITSM best practices are classified into five core perspectives:
- Service strategy
- Service design
- Service transition
- Service operation
- Continuous service improvement
At its core, enterprise architecture is about continuous business alignment and forward-looking planning towards effective data governance and business transformation.
Enterprise architecture: driving how data create value
Nightingale (2009) introduced the 7 principles of enterprise architecture thinking to guide organizations towards achieving sustainable transformation:
- Adopt a holistic approach to enterprise transformation
- Identify relevant stakeholders and determine their value propositions
- Focus on enterprise effectiveness before efficiency
- Address internal and external enterprise interdependencies
- Ensure stability and flow within and across the enterprise
- Cultivate leadership to support and drive enterprise behaviors
- Emphasize organizational learning
Enterprise architecture principle: focus on effectiveness before efficiency.
Effective data governance fosters better ways of working

Enterprise architecture: 9-block value grid
Data Continuity
Performing product development and operational maturity assessment, identifying opportunities for improvement, critical success factors and associated metrics
Stakeholders
Building capability and enterprise data alignment with stakeholder map, defining and driving data governance, managing capability implications across business functions
Change Strategy
Defining value statements based on expected change, aligning digitalisation and integration roadmaps, from education to data migration, archiving and decommissioning strategies
Value drivers
Building the business value realisation strategy, linking to the capability implementation roadmap to address current and future imperatives, pain point and risk mitigations
Master Data Strategy
Driving single source and single version of truth clarity, identifying configuration items, building data continuity and linkages across enterprise platforms and system interfaces
Operating Model
Assessing how the business operates, internally across teams and with the supply chain, defining how the change will affect current operations and how value will be realised
Portfolio Synergies
Defining product modularity, driving platformisation, mapping business processes and capabilities, improving knowledge capitalisation and standardisation and talent development
Business Capabilities
Understanding capability and improvement requirements, mapping user stories and business processes across functions, defining change roadmaps and deployment strategies
Decision-Making
Assessing change assumptions and interdependencies, mapping prioritization decisions, building awareness, initiating transformation governance and tracking effectiveness
Strategic Alignment
- How does the business currently operates?
- What is the current application and process landscape?
- What are the core strategic enterprise capabilities?
- Who are the process and data owners, and the key interdependencies across these capabilities?
- How are external parties interacting with enterprise platforms?
- What gaps or overlaps exist across capabilities, internally, and when collaborating with the supply chain?
- What is the cost of ownership and how does it align to the level of support service is provided by vendors and partners?
- Is there an improvement and evolution roadmap in place to account for industry best practices and technology advances?
Process Analysis
Are existing processes documented and purposely managed with current key user groups?
- How effective is the current operating governance?
Is process maturity and adherence effectively governed across business functions and projects?
What education programs and onboarding trainings are supporting the user communities?
How is data quality governed, within each programs or project, and across projects?
How are standards and data usage governed across business processes and supportive platforms?
What is regulated / mandated vs open for user-led adaptation?
Business Analytics
What are the success factors and key performance metrics to drive delivery results?
How are these indicators interrelated across the relevant balanced scorecard?
What are essential KPI metrics currently measured, and how are they informing ongoing projects?
How is delivery health currently assessed?
What additional or new metrics should also be measured?
Is the relevant data available to measure operational health?
What data feeds should be enhanced to drive quality assurance?
What metrics relate to resource and process efficiency, and how do they compare with those used by other projects, what constitute best practice?
Aligning the business operating model is essential to maximize effectiveness and embed continuous learning and improvement across the organization.
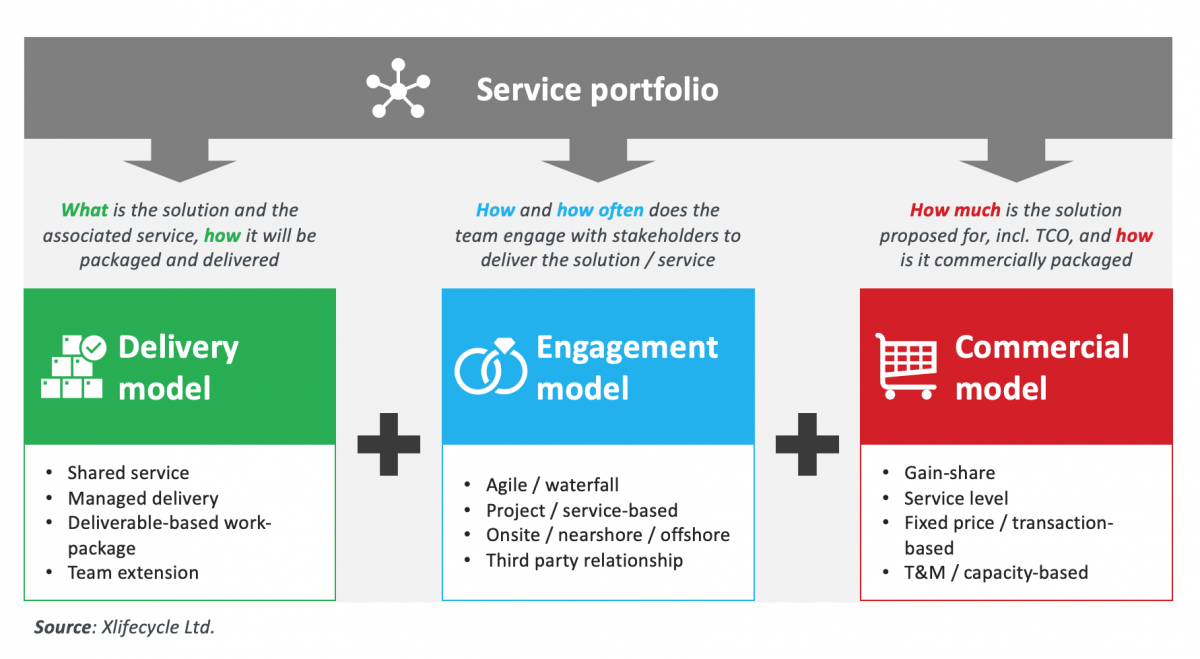
Read the blogSelecting the right service model implies answering questions such as: What is the proposed solution and associated service? How will they be packaged and delivered? How will the team engage with business and IT stakeholders to deliver the solution? How much will the solution cost, and what will be the total cost of ownership? How are products and services commercially bundled?
